The difference between the role and working principle of excitation transformer and ordinary transformer
2024-05-07 14:35:21
1. Overview of excitation transformer
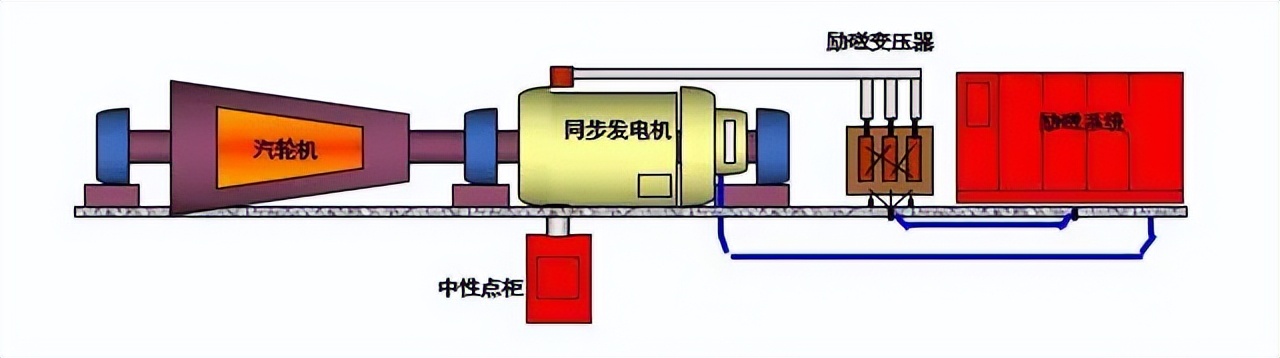
Excitation transformer is a kind of transformer device specially designed for generator excitation system, its main function is to convert the high voltage alternating current in the power system to the low voltage alternating current suitable for the generator excitation system. The excitation system is responsible for generating the magnetic field, which is the basis of the operation of the generator and drives the generator to produce electrical energy. The excitation transformer is usually installed at the output end of the generator, because the output voltage of the generator is high, and the operating voltage of the excitation system is relatively low, so the voltage needs to be reduced by the excitation transformer.
This transformer not only plays a role in reducing voltage, but also provides electrical isolation for the excitation system, ensuring safe operation between the generator and the power system. The design of the excitation transformer usually requires high insulation strength, good overload capacity and stability to ensure that the generator can work stably and efficiently under various conditions. It can convert three-phase alternating current into direct current through thyristor rectifier and other equipment, further control the generator excitation current, and realize the regulation of generator terminal voltage and reactive power.
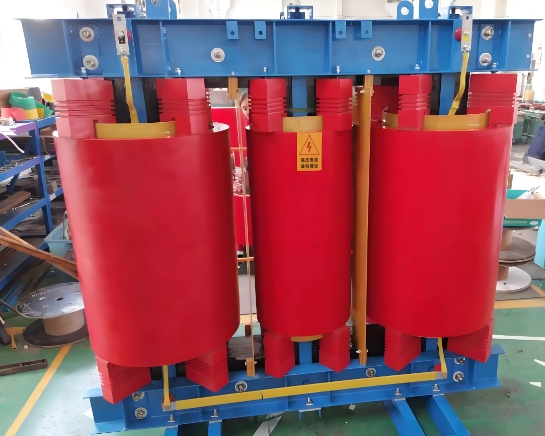

There are various types of excitation transformers, including epoxy resin cast dry transformers, alkali free glass fiber winding impregnated dry transformers, MORA type dry transformers and traditional oil immersed transformers, etc. Different types of transformers adapt to different working environments and performance requirements.
2. How it works
Working principle, the excitation transformer is usually connected to the auxiliary power supply side of the generator, accepting high-voltage alternating current from the power grid or other power sources, through the transformer, rectification and other links (if it is a DC excitation system), and finally provide the required DC current for the excitation winding of the generator, so as to establish and maintain the magnetic field strength required by the generator.
3. The key role of excitation transformer
Magnetic field control: The excitation transformer realizes the fine control of the generator magnetic field through the accurate regulation of the excitation current, which is the basis for ensuring the stability of the generator output voltage. When the power system fails or the load changes, the rapid adjustment of the excitation current can effectively suppress the voltage fluctuation and improve the dynamic stability of the system.
Improve efficiency and performance: By optimizing the design of the excitation transformer and reducing energy loss, the overall efficiency of the generator can be significantly improved. In addition, reasonable excitation control can also improve the power factor of the generator, reduce reactive power loss, and improve the overall performance of the system.
Protection of generator: excitation transformer with excitation control system, can react quickly in the generator overload or short circuit and other abnormal conditions, by adjusting the excitation current to avoid generator damage, play a role in protecting the generator.
Adapt to complex conditions: Modern excitation transformer design needs to meet the needs of different operating conditions, including extreme weather, frequency changes, voltage fluctuations, etc., to ensure that the generator can operate stably under various conditions.
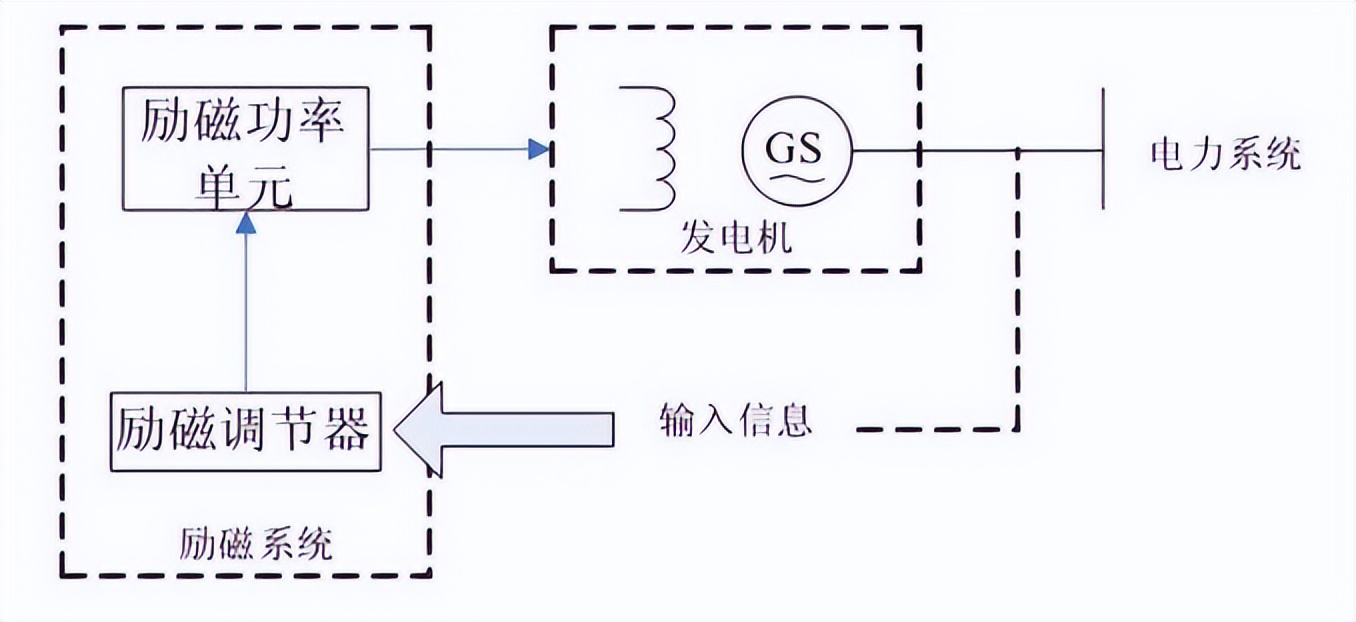
4. What is the difference between excitation transformer and ordinary transformer
Below, INFINITECH summarizes several key differences between excitation transformers and ordinary transformers:
In terms of purpose and function:
-
Excitation transformer: mainly used to provide stable AC excitation power for the excitation system of generators and transformers and other equipment, to ensure the establishment and regulation of the generator magnetic field, and then control the terminal voltage and reactive power of the generator.
-
Ordinary transformer: The main function is to change the size of AC voltage or current to meet the needs of different power transmission, distribution and use, and to achieve the matching of voltage levels.
In terms of design features:
- Excitation transformer: The design often has a larger core cross-sectional area and a lower voltage ratio to meet the requirements of high inductive reactance and low leakage reactance to ensure a stable supply of excitation current. It is usually equipped with precise regulation devices and feedback loops to control the excitation current.
- Ordinary transformer: The design is based on the specific application requirements, the core cross-sectional area and voltage ratio are more flexible, and there is no specific excitation current control requirement.
Performance requirements:
- Excitation transformer: requires higher stability and accuracy, with strong overload resistance, higher requirements for insulation grade, voltage resistance and overcurrent capacity, and more complex and sophisticated design and manufacturing technology.
- Ordinary transformers: Although also need to meet certain performance standards, but compared with the excitation transformer, its requirements may not be so strict, suitable for a wider range of voltage conversion scenarios.
Scope of application:
- Excitation transformer: specially used in generator excitation system, can not be easily replaced by ordinary transformers.
- Ordinary transformer: widely used in power transmission and distribution, industry, construction and other fields of voltage conversion, use is more common.
Energy saving and emission reduction:
- Excitation transformer: plays an important role in the power system, can help the system to save energy and reduce emissions by adjusting voltage, improving power factor and other means.
5. The advantages and disadvantages of dry excitation transformer and oil immersed excitation transformer are compared
Dry excitation transformer and oil-immersed excitation transformer have their specific application scenarios in power systems, and their respective advantages and limitations are as follows:
Advantages of dry excitation transformer
Dry transformers use resin or other solid insulating materials, no flammable insulating oil, so it has higher fire safety, especially suitable for installation in places with high fire protection requirements. There is no need to check and replace the insulation oil regularly like the oil-immersed type, and the maintenance workload is small, mainly for cleaning dust and checking the insulation condition. Dry-type transformers do not have oil pools, do not require special anti-leakage facilities, and can be installed in load centers or indoors, reducing space occupancy and voltage loss. There is no risk of oil leakage and no pollution threat to the environment. Modern dry-type transformers have reduced noise levels through improved design, but are usually still higher than oil-immersed transformers.
Disadvantages of dry excitation transformer
Due to the use of high-quality solid insulation materials, the cost is higher than that of oil-immersed transformers. It is usually larger and heavier than oil-immersed transformers of the same capacity. Relying on natural air cooling or forced air cooling, additional cooling measures may be required in high temperature environments, and the heat dissipation efficiency is not as good as that of oil immersion. Dry-type transformers are more sensitive to wet and dusty environments than oil-immersed transformers and require better protective measures.
Advantages of oil-immersed excitation transformers
Oil-immersed transformers are cheaper to manufacture, especially in high-capacity applications. As a cooling medium, oil can effectively absorb and dissipate heat, improve the thermal efficiency and continuous operation of the transformer. For large capacity transformers, oil-immersed transformers are usually smaller and lighter. With proper maintenance, oil-immersed transformers can provide long-term stable service with a long life.
Disadvantages of oil-immersed excitation transformers
Oil-immersed excitation transformers contain combustible insulating oils, which are at risk of fire and explosion and require special safety precautions. Regular inspection of oil quality, oil treatment and replacement is required, and maintenance costs are high. Due to potential oil leakage problems, there is a risk of pollution to the environment, and it is not suitable for installation in some sensitive areas. Usually installed outdoors or in a separate transformer room, the flexibility is not as good as dry transformers.
Summary: The choice of dry or oil-immersed excitation transformer needs to be determined according to the specific application environment, safety requirements, cost budget and maintenance conditions.
6. Excitation transformer common faults and solutions
Below, INFINITE summarizes some typical fault situations of excitation transformers and their treatment methods:
(1) Encourage failure
Causes: the starting button on time is insufficient, the generator residual voltage is too low, the power cabinet pulse switch position is wrong, the AC power supply of the rectifier bridge is not input, and the synchronous transformer fuse is not reset.
Solution: Ensure that the excitation button continues to be on for enough time (such as more than 5 seconds), remove the residual voltage excitation function, use the auxiliary power supply to start the excitation, correctly set the power cabinet pulse switch, check and restore the power supply on the high voltage side and the low voltage side of the excitation, and reset the synchronous transformer fuse holder.
(2) The output of phase shift pulse control voltage is abnormal
Cause: The excitation power supply is abnormal, the given value or measured value (generator voltage or excitation current) is abnormal.
Solution: Check whether the excitation power supply is stable, verify the accuracy of the given value and the measured value, and ensure that the adaptation unit works normally.
(3) Failure caused by environmental factors
Causes: temperature change, vibration, oxidation of components.
Solution: Regularly use an oscilloscope to check the integrity of the rectifier waveform, use a multimeter to detect the performance of thyristor and other components, strengthen maintenance, and replace damaged components in time.
(4) excitation transformer vibration and core temperature rise abnormal
Cause: The secondary side load is unbalanced.
Solution: Check the wiring of the excitation transformer after shutdown and power off to ensure load balance, check and repair possible mechanical problems, such as tightening loose parts.
(5) Starting overpressure
Reasons: excitation transformer phase sequence error, PT feedback voltage loop fault, residual voltage excitation loop did not exit correctly, regulator output pulse phase confusion.
Solution: Check and adjust the phase sequence of the excitation transformer, repair the fault of the PT loop, ensure the correct control of the residual voltage excitation loop, and correct the output pulse phase of the regulator.
(6) The power cabinet is faulty
Cause: low wind, relay problems.
Solution: Check the wind pressure system to ensure that the wind pressure is within the specified range, and repair or replace the faulty wind pressure relay.
In response to these failures, it is important to perform regular preventive maintenance, including checking electrical connections, monitoring operating parameters, cleaning and inspecting components, and making necessary component replacements as recommended by the manufacturer.
7. How to correctly select and maintain the excitation transformer
Correct selection and maintenance of excitation transformer is the key to ensure the stable operation of power generation system. Here are some important guidelines for selecting and maintaining an exciting transformer:
Select the excitation transformer
-
Determine the electrical characteristics and power requirements: First, according to the specifications of the generator and the requirements of the power system, select the appropriate voltage level, phase number, and ratio of the excitation transformer. To ensure that the transformer can provide sufficient excitation current under all working conditions, the voltage requirement of excitation cap value is considered when the generator is excited strongly.
-
Structure and environmental adaptability: Consider the size, weight, installation location (indoor/outdoor) and environmental requirements (such as temperature, humidity, ventilation conditions) of the excitation transformer. Precautions against rain, dust, and lightning should be taken for outdoor installation. Precautions against heat dissipation and fire should be taken for indoor installation.
-
Performance and efficiency: Choose transformers with low loss and high efficiency characteristics, especially dry excitation transformers are often recommended because of their low maintenance and environmental protection characteristics. Consider the overload capacity of the transformer to ensure that it can cope with transient overload without compromising performance.
-
Protection function: Confirm that the excitation transformer is equipped with or compatible with the necessary protection devices, such as differential protection, overcurrent protection, overheat protection, etc., to enhance system safety.
-
Quality and after-sales service: Select excitation transformers with good market reputation and in line with international quality certification standards, while considering the manufacturer's after-sales service and technical support capabilities.
Routine maintenance of excitation transformer method
Regularly inspect the exterior and interior of the excitation transformer (if accessible) in accordance with the manufacturer's maintenance manual to remove dust and dirt and ensure that vents are unimpeded to prevent overheating. Regularly measure the insulation resistance, winding temperature rise, load current and voltage of the excitation transformer, as well as the stability of the excitation current to ensure that the electrical performance meets the requirements. Use monitoring equipment to monitor the operation parameters of the excitation transformer in real time, such as temperature, current, voltage, etc., to detect anomalies in time and take measures. Ensure that the use of the excitation transformer load does not exceed its rated capacity, to avoid long-term overload operation, so as not to cause overheating or accelerate aging.
Preventive maintenance is performed by regularly replacing wearing parts such as cooling fans, filters and insulation materials based on operating time and manufacturer recommendations. Emergency plans should also be developed in advance, including the preparation of backup excitation transformers and rapid switching mechanisms, in case the main transformer fails to quickly resume operation.